Highly scalable, real-time search, distributed and analytics open source search engine build on top of Lucene and is natively JSON + REST API. In this tutorial we’ll look at some of the key concepts when getting started with Elasticsearch [ES].
| Open Source |
| Based on Lucene |
| RESTful API |
| Highly configurable |
| Runs on the JVM |
| Data exploration |
| Distributed: Cluster, fail over, replication, and master election out of the box |
| Schema less: document based, automated type mapping, JSON |
Downloading and running ElasticSearch [ES]
ES can be downloaded packaged in various formats such as ZIP, DEB, RPM and TAR.GZ from elasticsearch.org. After downloading and extracting a package running it couldn’t be much easier, please noted Java runtime must be installed.
Running ElasticSearch on Windows
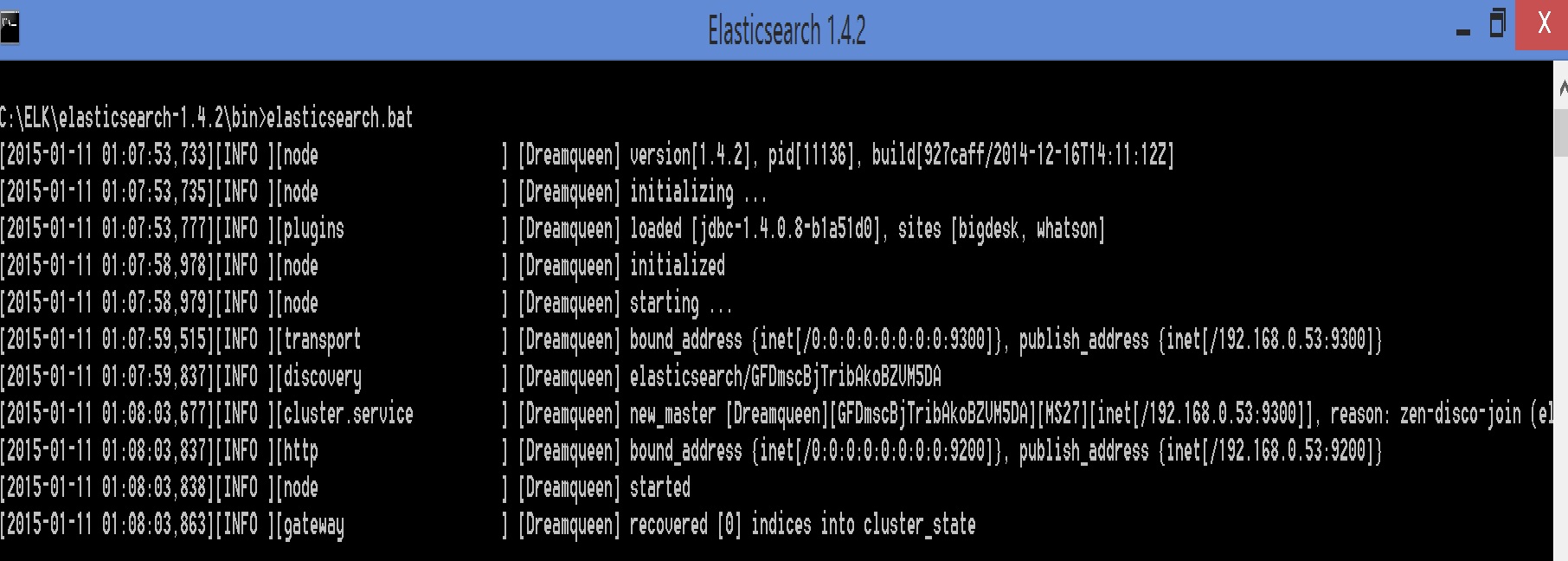
Navigate to the extracted directory to run ElasticSearch on Windows. We run C:\ELK\elasticsearch-1.4.2\bin\elasticsearch.bat [note this is my ES root directory]. This will start ElasticSearch running in the foreground in the console.
Just two things we have to make sure, one JAVA is installed and second we have a JAVA_HOME environment variable configured correctly.
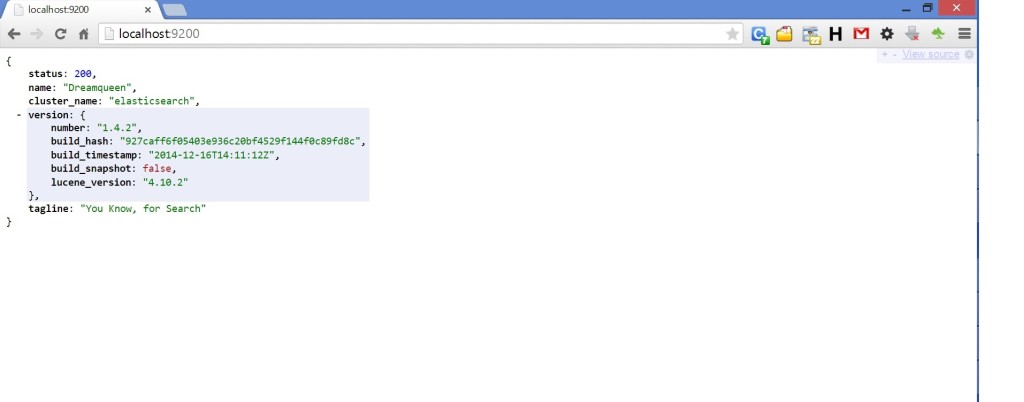
Let’s test ES is working using browser http://localhost:9200/
If we get status 200 it means – everything is fine.
What’s JSON output tells us?
- Ok: when it’s true, it means that request was successful.
- Status: HTTP error code that resulted from request. 200 means OK.
- Name: name of our ES instance. By default,it assign the node a random name.
- Version: The object here has a number field, which is version of ES we are currently running, and a snapshot_build field, which indicates if what we are running has been built from sources.
- Tagline: Contains first tagline of ES: “You Know, for Search.”
Useful Plugins
Now let’s install one of the ES plugin viz. ElasticSearch Head from http://mobz.github.io/elasticsearch-head/, this is an optional step.
C:\ELK\elasticsearch-1.4.2\bin>plugin -install mobz/elasticsearch-head
The Head plugin or elasticsearch-head is a web front end for browsing and interacting with an ES cluster. For more details on available plugins refer to the plugin guide.
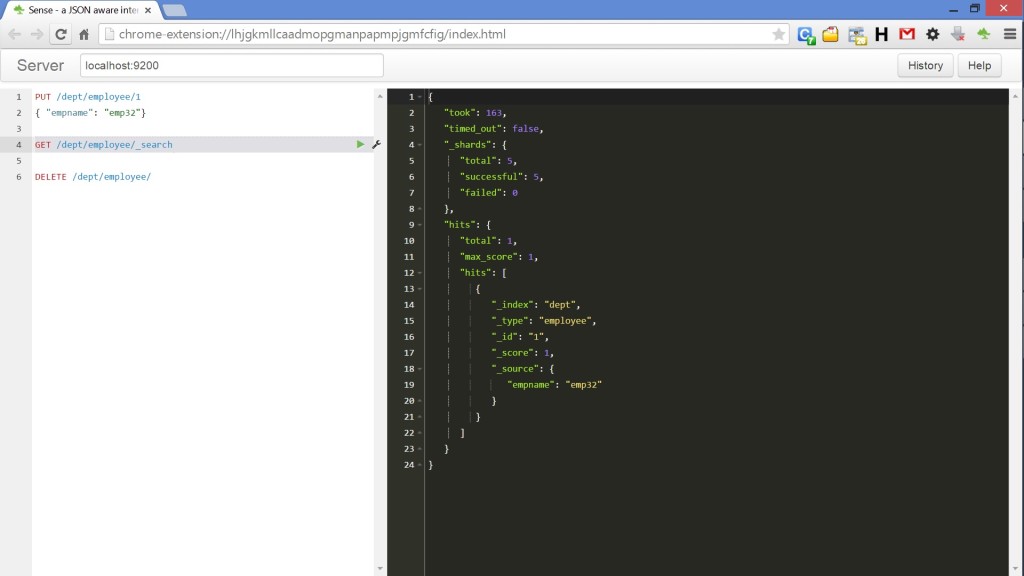
One more recommended Chrome plugin for quering ES is “Sense”. Sense provides a simple user interface for using ES REST API. It also has a number of features such as autocomplete for ES query syntax and copying & pasting requests in curl format. Below is how to get it.
Below are details on how to query ES using Sense for adding sample data to index.
We can verify data in ES head plugin as shown below.
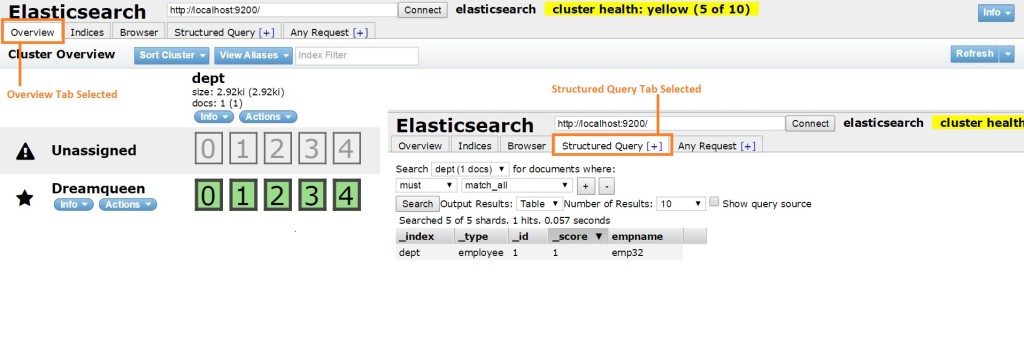
So now we are ready to play with ES and ready to dive in, for getting more out it.
Now What’s Next?
- Visit elasticsearch.org guide
- You may follow the elasticsearch.org blog
- Tutorials can be found at elasticsearch.org tutorials
- Find ES projects on github
- To use Elasticsearch with Java go to the elasticsearch.org Java API
- Marvel is a visual cluster health and metrics dashboard
- For graphical data analysis check out Kibana
- ES works seamlessly to collect, parse, index, and search logs with Logstash
Connect kubernetes pod to a GCS bucket using JS
To connect from a Kubernetes pod to a Google Cloud Storage (GCS)…Easiest way to run an LLM locally on your Mac
I recently sought an efficient method for local experimentation with Language Model…EKS cluster using an existing VPC
The eksctl command line tool can create a cluster by either command-line options or…kubectl Unable to connect to the server
When working with Kubernetes if you are getting Unable to conntect to…